Page 304 - English Grammar in Use
P. 304
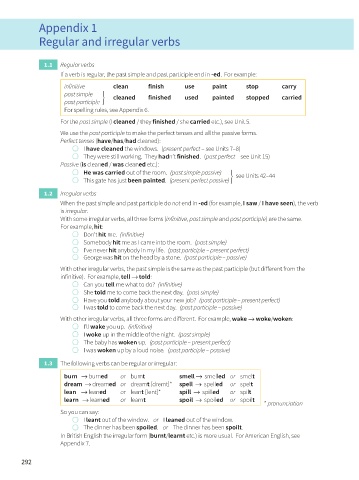
Appendix 1
Regular and irregular verbs
1.1 Regular verbs
If a verb is regular, the past simple and past participle end in -ed. For example:
infinitive clean finish use paint stop carry
past simple ⎫
⎬ cleaned finished used painted stopped carried
past participle ⎭
For spelling rules, see Appendix 6.
For the past simple (I cleaned / they finished / she carried etc.), see Unit 5.
We use the past participle to make the perfect tenses and all the passive forms.
Perfect tenses (have/has/had cleaned):
I have cleaned the windows. (present perfect – see Units 7–8)
They were still working. They hadn’t finished. (past perfect – see Unit 15)
Passive (is cleaned / was cleaned etc.):
He was carried out of the room. (past simple passive) ⎫
⎬ see Units 42–44
This gate has just been painted. (present perfect passive) ⎭
1.2 Irregular verbs
When the past simple and past participle do not end in -ed (for example, I saw / I have seen), the verb
is irregular.
With some irregular verbs, all three forms (infinitive, past simple and past participle) are the same.
For example, hit:
Don’t hit me. (infinitive)
Somebody hit me as I came into the room. (past simple)
I’ve never hit anybody in my life. (past participle – present perfect)
George was hit on the head by a stone. (past participle – passive)
With other irregular verbs, the past simple is the same as the past participle (but different from the
infinitive). For example, tell → told:
Can you tell me what to do? (infinitive)
She told me to come back the next day. (past simple)
Have you told anybody about your new job? (past participle – present perfect)
I was told to come back the next day. (past participle – passive)
With other irregular verbs, all three forms are different. For example, wake → woke/woken:
I’ll wake you up. (infinitive)
I woke up in the middle of the night. (past simple)
The baby has woken up. (past participle – present perfect)
I was woken up by a loud noise. (past participle – passive)
1.3 The following verbs can be regular or irregular:
burn → burned or burnt smell → smelled or smelt
dream → dreamed or dreamt [dremt]* spell → spelled or spelt
lean → leaned or leant [lent]* spill → spilled or spilt
learn → learned or learnt spoil → spoiled or spoilt
* pronunciation
So you can say:
I leant out of the window. or I leaned out of the window.
The dinner has been spoiled. or The dinner has been spoilt.
In British English the irregular form (burnt/learnt etc.) is more usual. For American English, see
Appendix 7.
292