Page 312 - English Grammar in Use
P. 312
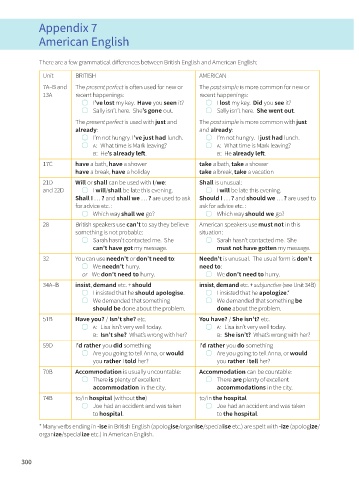
Appendix 7
American English
There are a few grammatical differences between British English and American English:
Unit BRITISH AMERICAN
7A–B and The present perfect is often used for new or The past simple is more common for new or
13A recent happenings: recent happenings:
I’ve lost my key. Have you seen it? I lost my key. Did you see it?
Sally isn’t here. She’s gone out. Sally isn’t here. She went out.
The present perfect is used with just and The past simple is more common with just
already: and already:
I’m not hungry. I’ve just had lunch. I’m not hungry. I just had lunch.
a: What time is Mark leaving? a: What time is Mark leaving?
b: He’s already left. b: He already left.
17C have a bath, have a shower take a bath, take a shower
have a break, have a holiday take a break, take a vacation
21D Will or shall can be used with I/we: Shall is unusual:
and 22D I will/shall be late this evening. I will be late this evening.
Shall I … ? and shall we … ? are used to ask Should I … ? and should we … ? are used to
for advice etc. : ask for advice etc. :
Which way shall we go? Which way should we go?
28 British speakers use can’t to say they believe American speakers use must not in this
something is not probable: situation:
Sarah hasn’t contacted me. She Sarah hasn’t contacted me. She
can’t have got my message. must not have gotten my message.
32 You can use needn’t or don’t need to: Needn’t is unusual. The usual form is don’t
We needn’t hurry. need to:
or We don’t need to hurry. We don’t need to hurry.
34A–B insist, demand etc. + should insist, demand etc. + subjunctive (see Unit 34B)
I insisted that he should apologise. I insisted that he apologize.*
We demanded that something We demanded that something be
should be done about the problem. done about the problem.
51B Have you? / Isn’t she? etc. You have? / She isn’t? etc.
a: Lisa isn’t very well today. a: Lisa isn’t very well today.
b: Isn’t she? What’s wrong with her? b: She isn’t? What’s wrong with her?
59D I’d rather you did something I’d rather you do something
Are you going to tell Anna, or would Are you going to tell Anna, or would
you rather I told her? you rather I tell her?
70B Accommodation is usually uncountable: Accommodation can be countable:
There is plenty of excellent There are plenty of excellent
accommodation in the city. accommodations in the city.
74B to/in hospital (without the) to/in the hospital
Joe had an accident and was taken Joe had an accident and was taken
to hospital. to the hospital.
* Many verbs ending in -ise in British English (apologise/organise/specialise etc.) are spelt with -ize (apologize/
organize/specialize etc.) in American English.
300